Understanding The Rise Of Remote Work
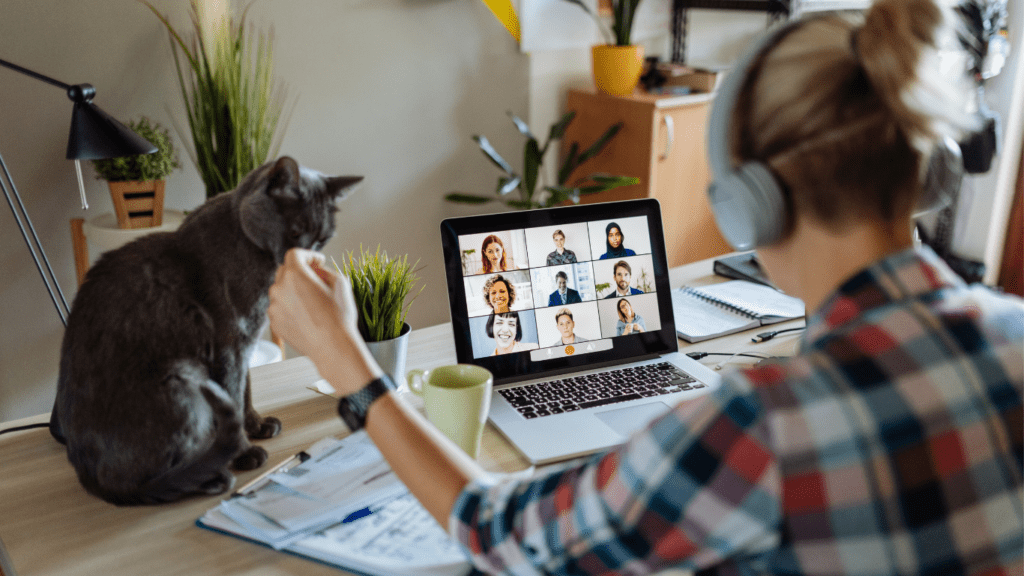
Remote work is transforming business landscapes and individual routines, redefining how economies operate. A combination of technological advancements and shifting preferences drives this major shift.
Key Drivers Behind The Remote Work Trend
- Global Health Events
Major health crises, such as the COVID-19 pandemic, accelerated remote work adoption. In 2020, over 40% of US employees worked remotely during the peak of the pandemic, according to Pew Research Center. - Employee Preferences
A significant number of workers favor flexibility over traditional structures. For example, a FlexJobs survey found that 65% of professionals prefer fully remote roles. - Cost Implications
Businesses save on office overhead, while employees cut commuting expenses. Global Workplace Analytics notes companies save $11,000 annually per part-time remote worker. - Access To Global Talent
Employers now hire from diverse locations, leveraging skills previously inaccessible. Remote work platforms simplify recruitment from international markets.
- Communication Tools
Platforms like Zoom, Microsoft Teams, and Slack streamline remote team collaboration. Zoom saw a 2900% surge in daily meeting participants within four months in 2020. - Cloud Computing
Cloud services like Google Workspace and Microsoft 365 ensure teams access data seamlessly. By 2023, the global cloud computing market exceeded $600 billion, Statista reports. - Security Enhancements
Virtual private networks (VPNs) and multi-factor authentication (MFA) protect sensitive information in remote setups. Investment in cybersecurity grew 15% annually after 2020. - Automation And AI
AI tools help streamline remote workflows, with software like Asana and Notion managing tasks efficiently. Workspace automation reduces manual dependency, boosting productivity.
Economic Impacts Of Remote Work
Remote work trends are driving significant shifts in economic structures globally. These changes affect job markets, urban and rural economies, and local industries like real estate and small businesses.
Implications For Global Job Markets
Remote work is expanding access to a global talent pool. Businesses now recruit candidates from diverse geographic regions, reducing reliance on local labor markets. According to McKinsey, 20-25% of the workforce in advanced economies can work remotely three to five days a week, increasing employment opportunities in underrepresented areas. Wage competition is also intensifying, with companies balancing cost savings against fair compensation for international employees.
Employers are adapting to manage cultural differences and varying labor laws. Platforms like Upwork and Turing streamline cross-border hiring, giving companies the tools they need to onboard remote employees quickly. This global approach is fostering skills diversification as professionals learn to operate in multinational environments.
Changing Urban And Rural Economies

Urban economies are experiencing declines in demand for services like public transit and downtown retail due to fewer commuters. The American Public Transportation Association reported a 36% drop in public transit ridership between 2019 and 2022. Conversely, rural and suburban areas are seeing growth as remote workers relocate for lower housing costs and better quality of life.
Spending patterns are shifting geographically. Local economies near popular relocation destinations benefit from increased consumer activity that boosts small businesses, real estate markets, and infrastructure development. Fiscal balances are adjusting as tax bases diversify, redistributing economic resources between traditionally urban centers and emerging rural hubs.
Influence On Real Estate And Local Businesses
The real estate sector is adapting to rising demand for home office setups and reduced demand for commercial spaces. A Deloitte study found that 68% of companies are rethinking office footprints, reducing leasing costs and exploring hybrid spaces. Suburban housing markets have seen value increases as remote work reshapes housing preferences.
Local businesses reliant on office workers for revenue face challenges, while firms catering to residential areas thrive. Coffee shops, co-working spaces, and delivery services align their offerings for remote lifestyles. E-commerce growth continues to expand, with retail businesses leveraging digital platforms for sustained engagement.
Opportunities In A Remote-First Economy
Remote-first shifts create unique opportunities for businesses, workers, and local economies. Embracing these changes sparks advancements in technology, skill development, and sustainable practices.
Innovation In Remote Work Technologies
Technological advancements drive efficiency in remote work environments. Tools like:
- Slack
- Trello
- Asana
simplify task management, enabling seamless project coordination. Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) are emerging, providing immersive environments for remote collaboration. By 2025, VR adoption in professional settings is projected to exceed $8 billion, enhancing team engagement. Enhanced cybersecurity protocols, including zero-trust frameworks, ensure secure operations as remote networks expand.
Reskilling And Workforce Development
Upskilling initiatives help workers stay competitive in a global job market. Remote-first models highlight digital skills such as proficiency in Zoom or Google Workspace and specialized technical expertise like coding or data analysis. Over 50% of employers globally have prioritized reskilling programs, according to a World Economic Forum report. Businesses invest in online learning platforms like Coursera or Udemy to train employees, addressing skill gaps and ensuring workforce adaptability.
Sustainability And Reduced Carbon Footprints
Remote work reduces commuting-related emissions, promoting environmental sustainability. A Global Workplace Analytics report reveals that if 50% of the US workforce telecommuted half the time, greenhouse gas emissions could decrease by 54 million tons annually. Fewer office buildings lower energy consumption and waste production, while remote-first policies encourage greener lifestyle choices, including reduced transportation and decentralized energy usage.