Understanding The Science Of Happiness
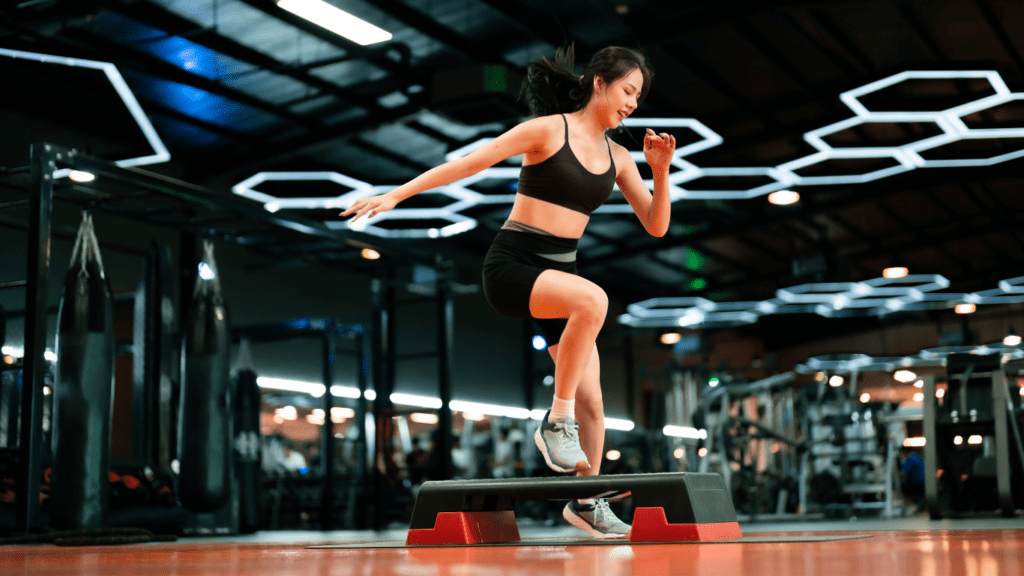
Exploring the science behind happiness reveals its critical role in shaping health, longevity, and decision-making. Recognizing its components helps build a stronger foundation for a positive mindset.
The Definition Of Happiness
Happiness is a subjective state comprised of emotional well-being, life satisfaction, and a sense of meaning. According to the American Psychological Association, it involves frequent positive emotions like joy or contentment and the absence of extensive negative emotions. Psychologists often categorize it into two components: hedonic happiness, which centers on pleasure and comfort, and eudaimonic happiness, rooted in purpose and achievement. Both dimensions contribute to a holistic understanding of happiness.
Why Happiness Matters
- Happiness impacts physical and mental health, social connections, and productivity.
- Studies, including one published in the Journal of Happiness Studies, show that happier individuals face reduced stress levels and enhanced immune responses.
- Stronger relationships are common because positivity fosters empathy and trust.
- In workplace settings, happiness drives motivation and efficiency, as noted in a Harvard Business Review study, improving overall performance.
- Happiness isn’t just an abstract concept; its influence extends to measurable outcomes in daily life.
The Psychology Behind A Positive Mindset
A positive mindset involves cognitive and emotional patterns that influence how we perceive and respond to life’s challenges. Psychological factors and behaviors work together to create this mindset, fostering well-being and success.
Key Components Of A Positive Mindset
Several psychological elements consistently contribute to a positive mindset:
- Gratitude: Regularly expressing gratitude strengthens emotional resilience and enhances happiness levels. For example, maintaining a gratitude journal can create long-term shifts in one’s mental outlook.
- Self-Awareness: Recognizing and regulating thoughts and emotions reduces negativity and encourages constructive behavior.
- Focus On Strengths: Concentrating on personal strengths instead of weaknesses builds confidence and optimism, promoting personal growth.
- Cognitive Reframing: Reinterpreting adverse situations positively shapes perceptions, fostering better problem-solving skills.
These components are vital for developing habits that reinforce positivity over time.
The Role Of Optimism And Resilience
Optimism and resilience are key drivers of psychological well-being and adaptability:
- Optimism: An optimistic outlook increases motivation, improves mental health, and enhances decision-making. Positive expectations about outcomes can activate reward processing in the brain, which reinforces proactive behavior.
- Resilience: Resilient individuals recover faster from stress and adversity as they use positive coping mechanisms and view setbacks as temporary challenges. For example, practicing mindfulness or seeking social support can bolster resilience.
Together, optimism and resilience form the foundation for maintaining a positive mindset even in the face of challenges.
Practical Strategies To Cultivate Happiness

Implementing proven methods enriches emotional well-being and nurtures a positive mindset. These strategies encourage healthy habits, driving sustained happiness.
Mindfulness And Meditation
Engaging in mindfulness and meditation improves focus and emotional balance. Mindfulness involves being fully present, observing thoughts and feelings without judgment. Meditation trains the mind to maintain calm and clarity, reducing stress. Research from the American Psychological Association shows that consistent mindfulness practices lower cortisol levels and enhance mood. A simple way to start is with 10-minute daily guided meditations.
Gratitude Practices
Regular gratitude habits strengthen positivity. Listing three things I’m grateful for daily shifts attention toward positive experiences. Psychology Today notes that gratitude boosts dopamine release, reinforcing feelings of joy. Writing gratitude letters to friends or mentors creates emotional bonds while enhancing overall happiness. Practicing gratitude consistently transforms perspective over time.
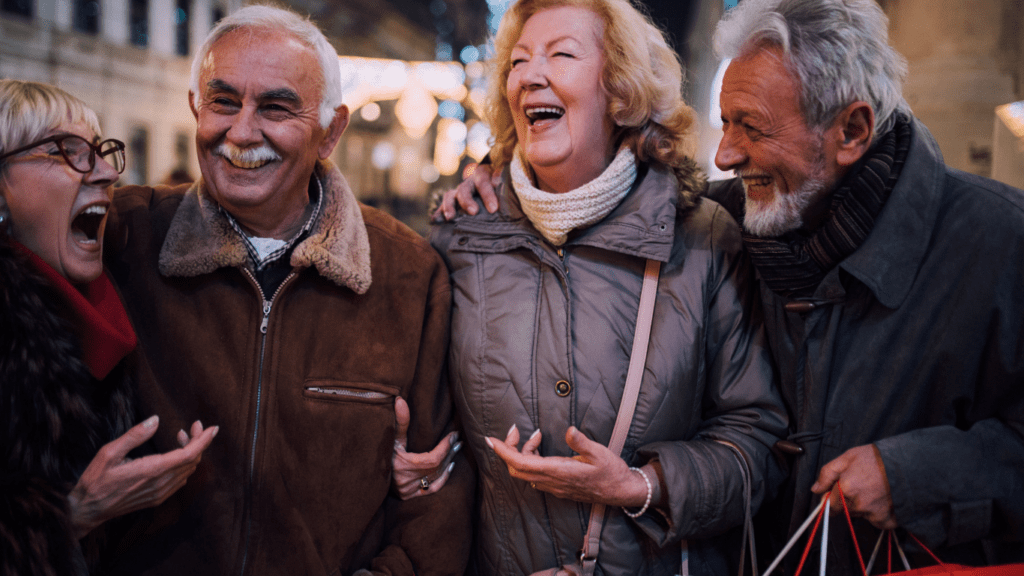
Building Strong Social Connections
Cultivating meaningful relationships fosters happiness and resilience. Connecting with supportive individuals boosts oxytocin production, according to Harvard Health. I focus on spending quality time with family and friends, engaging in group activities, or joining social clubs. Acts of kindness within these connections deepen trust and satisfaction. By prioritizing vibrant social networks, happiness becomes more sustainable.
The Impact Of Lifestyle Choices
Lifestyle choices play a critical role in shaping happiness and fostering a positive mindset. Decisions related to physical and mental well-being significantly influence emotional resilience and overall satisfaction.
Exercise And Physical Health
Regular exercise strengthens both the body and mind by promoting the release of endorphins, improving mood, and reducing stress. Studies indicate that even moderate physical activity, such as brisk walking for 150 minutes per week, can enhance mental well-being and counteract symptoms of anxiety and depression. Activities like yoga or strength training also improve sleep quality and boost energy, supporting emotional balance.
Consistent physical movement promotes brain health by encouraging neuroplasticity and growing new nerve connections. Research shows physically active individuals experience improved focus and memory, which positively impacts decision-making and stress management. I aim to include activities I enjoy, such as swimming or cycling, to make exercise sustainable and enjoyable.
Nutrition And Brain Health
Diet significantly affects brain function, mood stability, and long-term emotional health. Nutrient-rich foods, including fatty fish, leafy greens, and berries, support cognitive performance by providing essential vitamins and antioxidants. Omega-3 fatty acids, in particular, are associated with reducing symptoms of depression and increasing serotonin production.
Poor eating habits, like excessive sugar or processed food consumption, contribute to mood swings and fatigue by disrupting blood sugar levels. I prioritize balanced meals including proteins, healthy fats, and fiber to enhance mental clarity and prevent energy crashes. Hydration also plays a crucial role, as even mild dehydration has been linked to reduced focus and irritability.